COVID19
- CKD higher risk for hospitalization (risk ratio, 1.6; 95% confidence interval, 1.3 to 1.9)
- mortality (risk ratio, 1.3; 95% confidence interval, 1.3 to 2.0)
- Never forget The initial RRT/Tx mortality in UK was 25% of hospital admissions ( pre vaccine era)
Vaccines
- RRT antibody response is 89% relative to healthy controls- wanes over time.
- Tx recipients, antibody response ~ 35% with small increments to repeat vaccination.
- Omicron and later variants require higher antibody titers are required for viral neutralization
Drugs
Paxlovid
- Nirmatrelvir is an orally administered antiviral agent inhibiting the SARS-CoV-2 3-chymotrypsin–like cysteine protease enzyme (Mpro), also referred to as 3C-like protease or nsp5 protease, which renders the protein incapable of processing polyprotein precursors and prevents viral replication
- Ritonavir is a CYP3A4 inhibitor and enhances nirmatrelvir’s bioavailability
- EPIC-HR showed in high risk, mild-mod (non hospitalised) patients f COVID-19–related hospitalization or death by day 28 was 89% lower in the treatment group than in the placebo group. There were 13 deaths, all in the placebo group.
- No eGFR <30 in the group
Prescribing Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir for COVID-19 in Advanced CKD
- Nirmatrelvir has a molecular mass of 499.5 D, 35% is approximately excreted by the kidneys, and it is 70% protein bound. Ritonavir is mostly hepatically metabolized. Thus Nirmatrelvir will accumulate.
- Adverse events reported by >1% of the participants were dysgeusia, nausea, vomiting, headache, diarrhea, and fever. In the phase 2 study with eGFR <30 ml/min per 1.73 m2, two of eight patients (25%) reported dysgeusia and dry mouth compared with none in the other arms with higher kidney function
- Hemodialysis will clear a clinically insignificant amount of nirmatrelvir(, on the basis of what is known about its molecular size, protein binding, and volume of distribution. (prob)
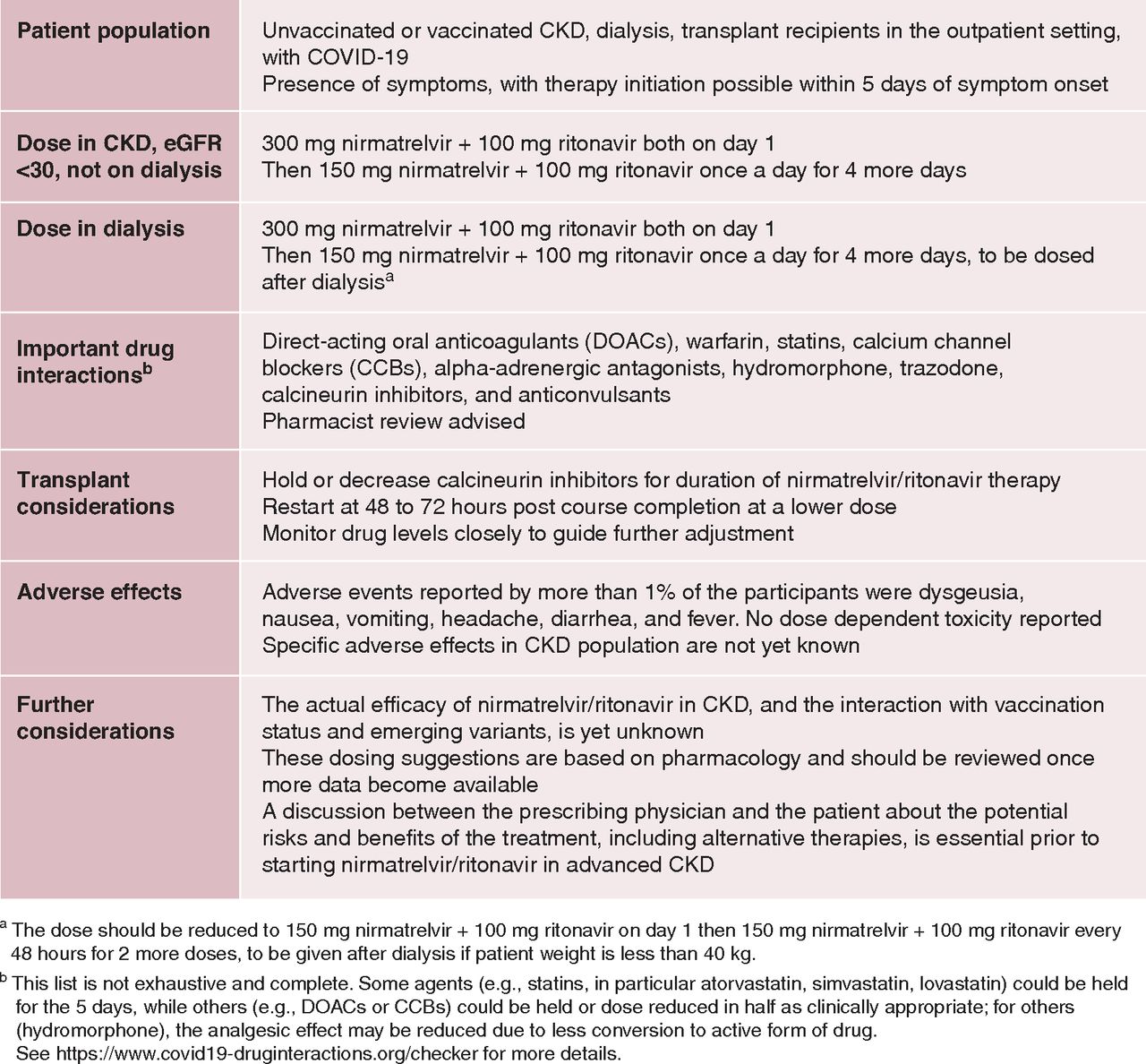
Summary of CKD/HD regime from Swampnil’s
paper
NB - Drug interactions: potent CYP3A4 inhibitor and an inducer of other cytochrome p450 enzymes - If used in Tx patients even with eGFR >60 can spike tac levels 10x. proceed very cautiously / stop tac if used at all. - Avoid in hepatic dysfn or eGFR <30 in tx setting.

Summary of tx guidance